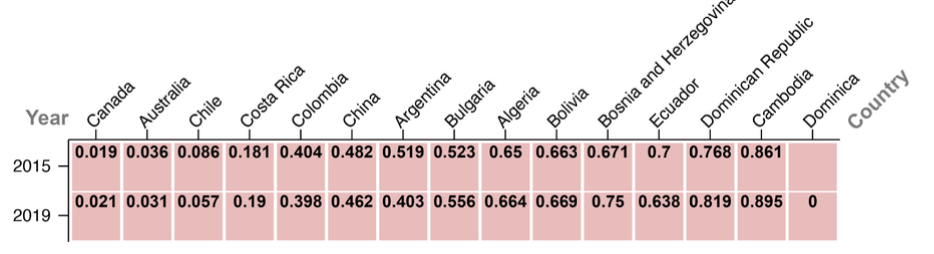
data mapping
BRIEF
This project aimed to analyze the intricate relationship between corruption and societal progress through a comprehensive examination of global data. Our research highlighted that corruption not only hinders economic growth but also exacerbates inequality and environmental degradation.
AREAS OF ANALYSIS
To structure our investigation, we focused on four critical aspects:
Political Corruption: Examining how unethical governance practices erode public trust, weaken policy effectiveness, and misallocate resources.
Bribery Rates: Analyzing the prevalence of bribery across regions and its direct impact on economic disparity and public services.
Corruption Perception: Assessing global perception indices to understand how corruption is viewed by citizens and how these perceptions influence societal development.
Land Degradation: Investigating how corruption in land management contributes to environmental harm, reduces agricultural productivity, and reinforces inequality.
VISUAL STRATEGIES
Layered Approach: Each topic was represented as an independent yet interconnected visual layer, enabling a nuanced exploration of corruption’s effects.
Dynamic Visual Aids: Charts, heat maps, and infographics illustrated key trends and regional disparities.
Interactive Key: A comprehensive legend helped readers interpret data accurately and efficiently.
By leveraging design as a tool for clarity, our project translates intricate global challenges into actionable insights, making the fight against corruption more transparent and data-driven.
FINDINGS
Economic Consequences: Corruption slows GDP growth, deepens poverty, and widens inequality.
Governance Matters: Countries with strong institutions and transparent policies are more effective in curbing corruption.
Environmental Impact: Corruption in land management accelerates land degradation, with far-reaching ecological and social repercussions.
TAKEAWAYS
This project underscores the far-reaching effects of corruption, revealing its impact on economies, societies, and ecosystems. Our findings highlight the urgent need for:
Robust Governance: Strengthening institutional transparency and accountability to combat corruption.
Public Engagement: Encouraging active civic participation in promoting integrity and systemic change.
DESIGN IN COMMUNICATION
Design played a crucial role in transforming complex data into accessible and engaging narratives. Through thoughtful visualization, we provided a resource that informs policymakers, educators, and advocates.